Are you seeking for 'compound assignment'? You can find all the information here.
The compound-assignment operators combining the simple-assignment hustler with another multiple operator. Compound-assignment operators perform the performance specified by the additional operator, past assign the outcome to the leftist operand. For instance, a compound-assignment construction such as expression1 += expression2
Table of contents
- Compound assignment in 2021
- Compound assignment statement
- Compound assignment java
- Compound assignment operator
- Convert to compound assignment
- Organic compounds assignment quizlet
- Compound assignment operator overloading in c++ example
- Compound assignment in c++
Compound assignment in 2021
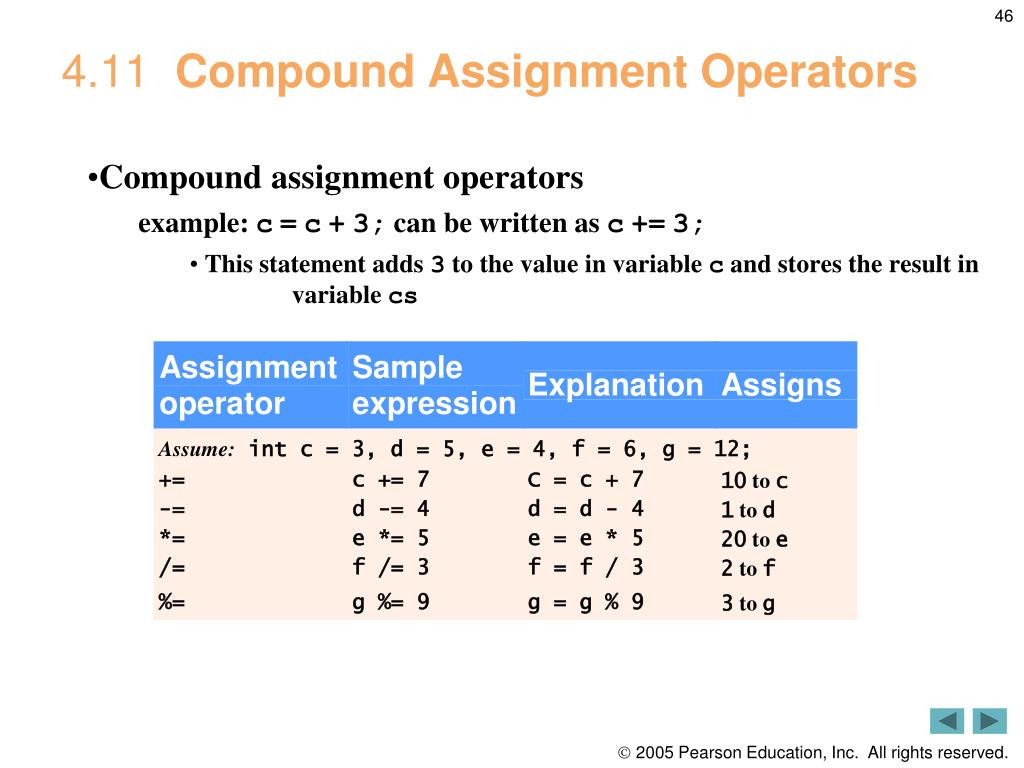 This image representes compound assignment.
This image representes compound assignment.
Compound assignment statement
 This picture shows Compound assignment statement.
This picture shows Compound assignment statement.
Compound assignment java
 This image demonstrates Compound assignment java.
This image demonstrates Compound assignment java.
Compound assignment operator
 This picture representes Compound assignment operator.
This picture representes Compound assignment operator.
Convert to compound assignment
 This image illustrates Convert to compound assignment.
This image illustrates Convert to compound assignment.
Organic compounds assignment quizlet
 This picture representes Organic compounds assignment quizlet.
This picture representes Organic compounds assignment quizlet.
Compound assignment operator overloading in c++ example
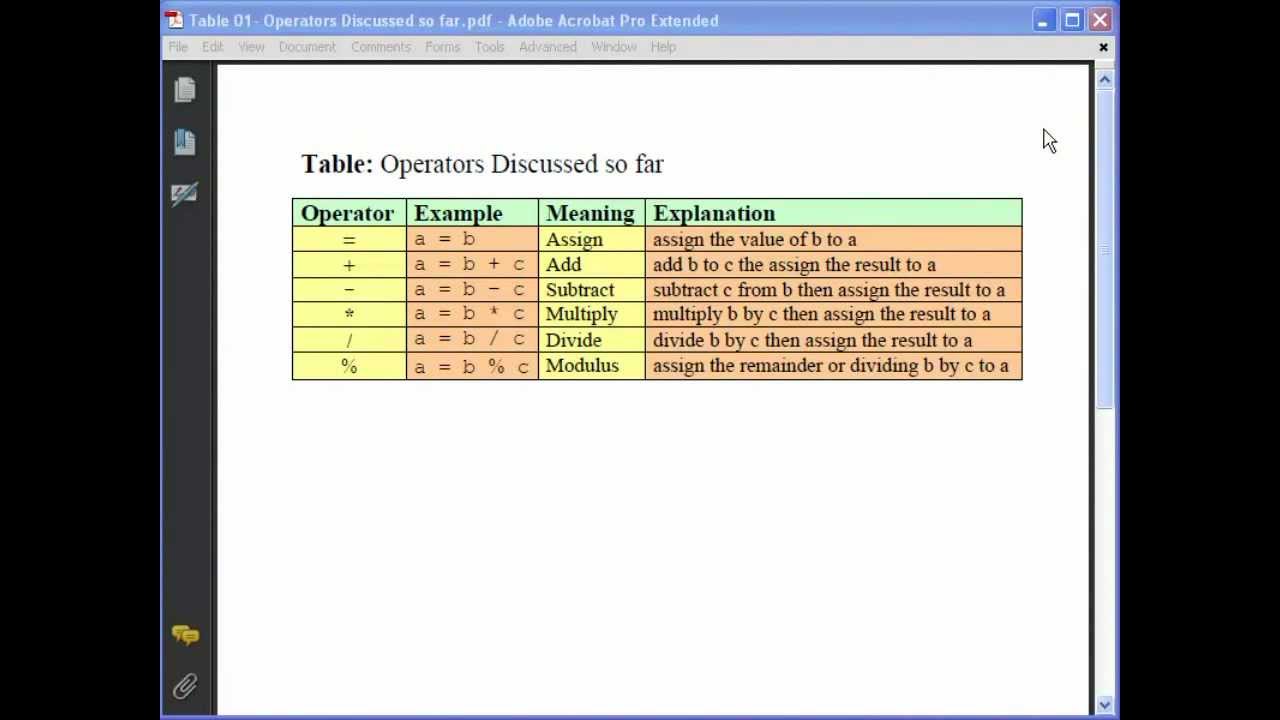 This picture shows Compound assignment operator overloading in c++ example.
This picture shows Compound assignment operator overloading in c++ example.
Compound assignment in c++
 This image illustrates Compound assignment in c++.
This image illustrates Compound assignment in c++.
Which is an example of a compound assignment?
The compound-assignment operators combine the simple-assignment operator with another binary operator. Compound-assignment operators perform the operation specified by the additional operator, then assign the result to the left operand. For example, a compound-assignment expression such as expression1 += expression2
Which is the right hand operand of compound assignment?
The addition-assignment ( +=) and subtraction-assignment ( -=) operators can also have a left operand of pointer type, in which case the right-hand operand must be of integral type. The result of a compound-assignment operation has the value and type of the left operand.
When do you use a compound assignment operator?
Compound-assignment operators provide a shorter syntax for assigning the result of an arithmetic or bitwise operator. They perform the operation on the two operands before assigning the result to the first operand.
Is the compound assignment expression the same as the expanded expression?
For example, a compound-assignment expression such as However, the compound-assignment expression is not equivalent to the expanded version because the compound-assignment expression evaluates expression1 only once, while the expanded version evaluates expression1 twice: in the addition operation and in the assignment operation.
Last Update: Oct 2021